A quick explanation about what is data structure and its types.
What is Data Structure?
A data structure is a way to store, organize, process and retrieve data in the computer memory. It’s arrange data and access it in an efficient way.
Types of Data Structure
Linear Data Structures
As the name says, the data are arranged sequentially or linearly. Each element points to its previous and next adjacent elements.
Array
An array is a static data structure with multiple fixed number of elements and the same data type that can be modified later. Each element has its own place/index in the list even though they shared the same variable name. In every index it’s possible to set a value and this value/element can be access by its specific index, helping to find the value in the list.
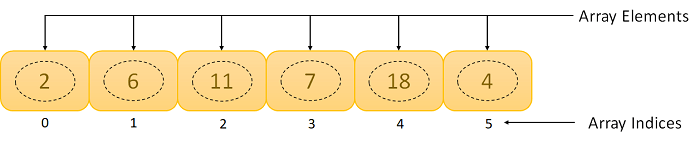
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(1)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(n)
- Deletion: O(n)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
Linked list
A linked list store a collection of data elements dynamically, separating them and stored consecutively in the memory. They are linked using pointers to refer to next element if singly linked list, doubly linked list also point to previous element.
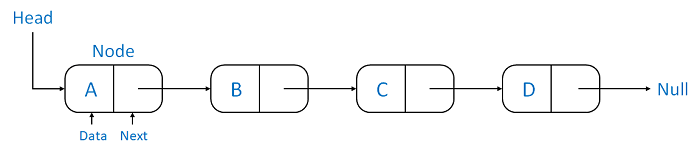
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(1)
- Deletion: O(1)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
Stack
Stack follows the order LIFO(Last In, First Out), which mean the first element inserted is the last to be removed. Entering data called push and retrieving data called pop in a stack. We can access only the Stack’s tops at any given time.

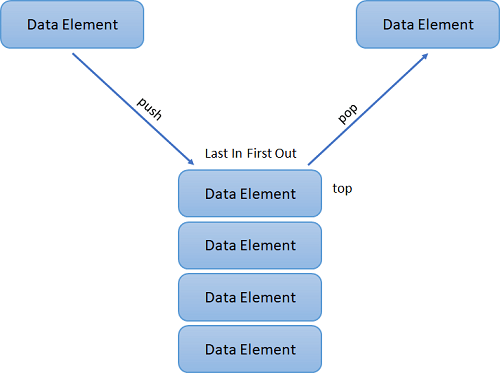
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(1)
- Deletion: O(1)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
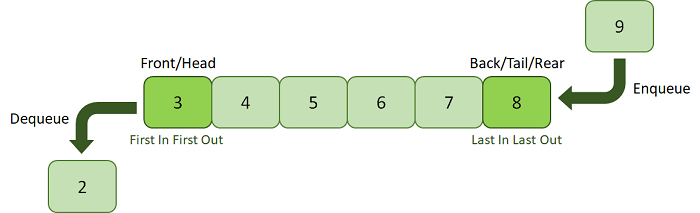
Queue
Queue follows the order FIFO(First In, First Out) which means the first element inserted is also the first to be removed. Insertion or Addition an element to the queue is called Enqueue while deleting or removing an element is called dequeue.
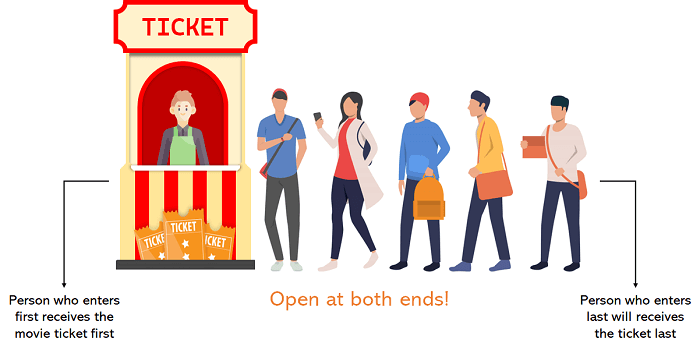
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(1)
- Deletion: O(1)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
Non-Linear Data Structures
The data are not placed sequentially or linearly. The elements point to multiples other elements.
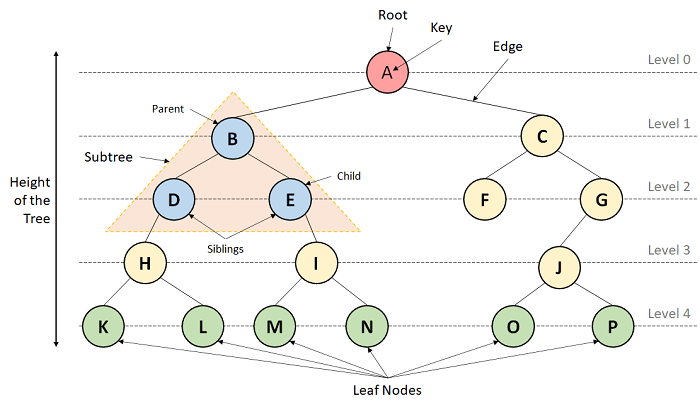
Tree
It contains a collection of nodes in a hierarchy, which every node parent has other 1 or 2 children, and so on for each child. It does not store the data sequentially but multiple levels.
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(n)
- Deletion: O(n)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
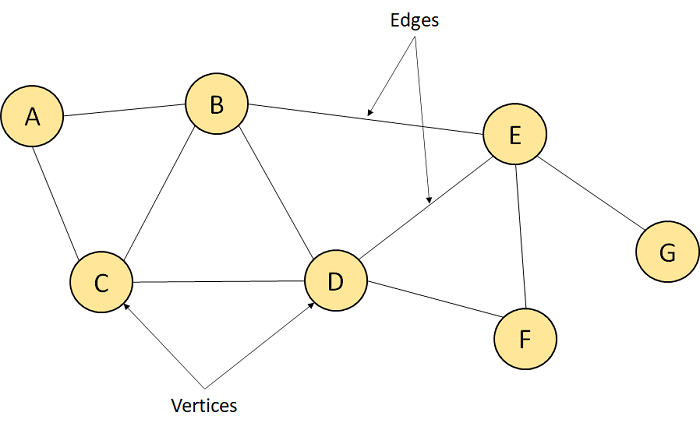
Graph
A graph doesn’t have root node and no standard order of arranged. It contains a finite number of nodes or vertices and the edges connecting them.
Time Complexity(Worst case scenario):
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion: O(n)
- Deletion: O(n)
Space Complexity(Worst case scenario: O(n)
References:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-data-structure-types-classifications-and-applications/
- https://www.javatpoint.com/data-structure-introduction
- https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/data-structure-tutorial/what-is-data-structure
